May 2024
How I Build a Chatbot with Amazon Lex and Lambda in 9 Steps
In this project, I used Amazon Lex to create a practical chatbot, BankerBot, to help the imaginary bank's customers check account balance and transfer money between accounts.
Here are some key concepts to review at the end of the project:
- 💡 Idle session timeout
- 💡 confidence score threshold
- 💡 intents
- 💡 utterance
- 💡 fallbackIntent
- 💡 slots
- 💡 Lambda function
- 💡 Alias
Step 1: Create a bot
- Navigate to Amazon Lex and click "Create Bot"
- Choose "Create a role with basic Amazon Lex permissions", This will create a policy that gives Amazon Lex permissions to call other AWS services, such as Lambda.
- Setup Idle session timeout. If you set idle session to 5 mins, that means the user's chatbot will end if he/her is idle or does not provide any input for 5 mins.
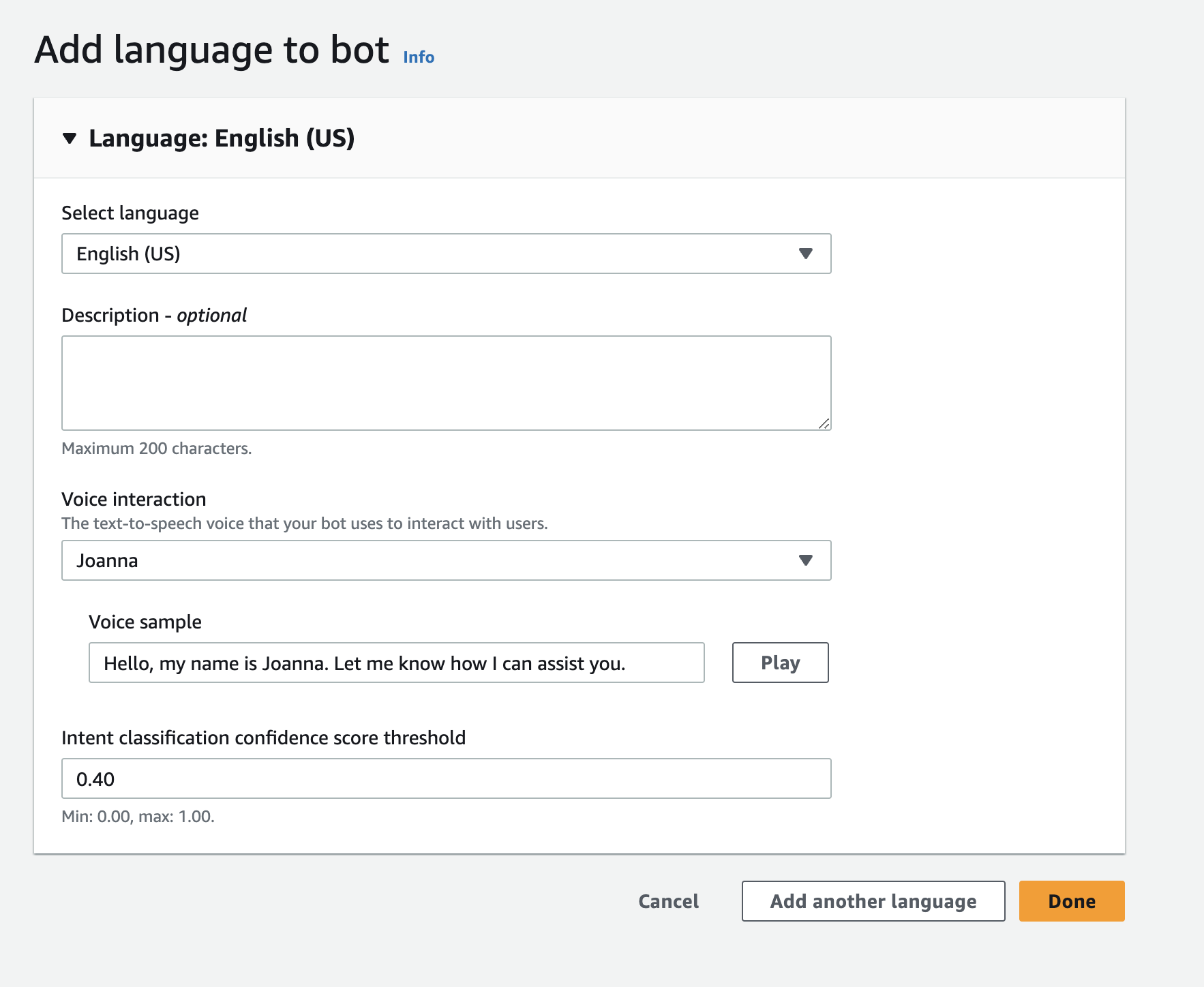
- Setup language, voice interaction and confidence score threshold.
- Done!
Key notes ✏️:
What's confidence score threshold?
The threshold score determins how confident the chatbot to understand user's input. A score of 0.4 means that the chatbot is at least 40% confident to understands what the user is asking. So if a user's input is ambiguous and the chatbot's confidence score is below 0.4, it will throw an error message.
Step 2: Create a Welcoming Intent
This intent is to let the chatbot welcomes a user when they say hello.
-
Add some sample utterances:
- Hi
- Hello
- I need help
- Can you help me?
-
Add the closing response to tell the bot what to respond to those utterances:
- Hi! I'm BB, the Banking Bot. How can I help you today?
-
Time to build and test the bot.
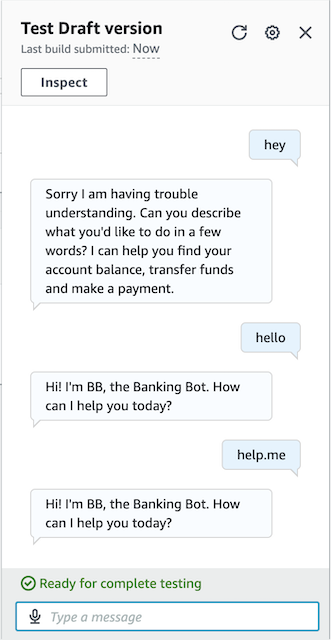
It can be seen that the bot is able to understand some of the phrase twist. But the input like "hey" is outside of the bot's confident score to understand. Next, we need to tell the bot what to respond if it doesn't understand user's intent.
Step 3: Setup FallbackIntent
To offer helpful prompts when the bot fails to understand the user, a FallbackIntent is setup for the bot to seek clarification.
-
Change FallbackIntent's closing response.
-
Time to build and test the bot again
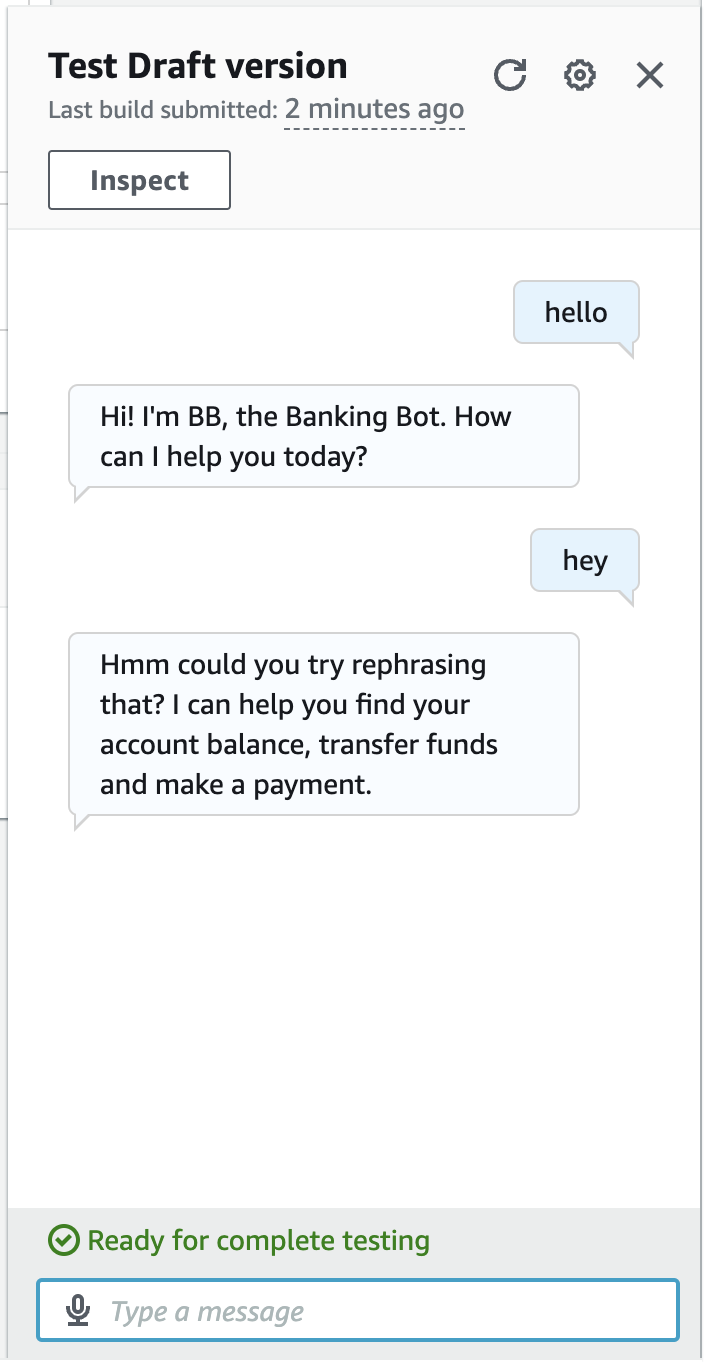
Step 4: Create Slot Types
In order to know which account a user wants to check, we need to set up slots that tells the bot what information we need to gather from the user.
Key notes ✏️:
What are slots?
Slots are information that a chatbot requires to fulfill a user's request, similar to filling out a form. For instance, to book a restaurant table, a chatbot needs details such as the restaurant name, date, time, and party size.
For this banker bot, I created a slot called "AccountType" that includes:
- Checking
- Savings
- Credit
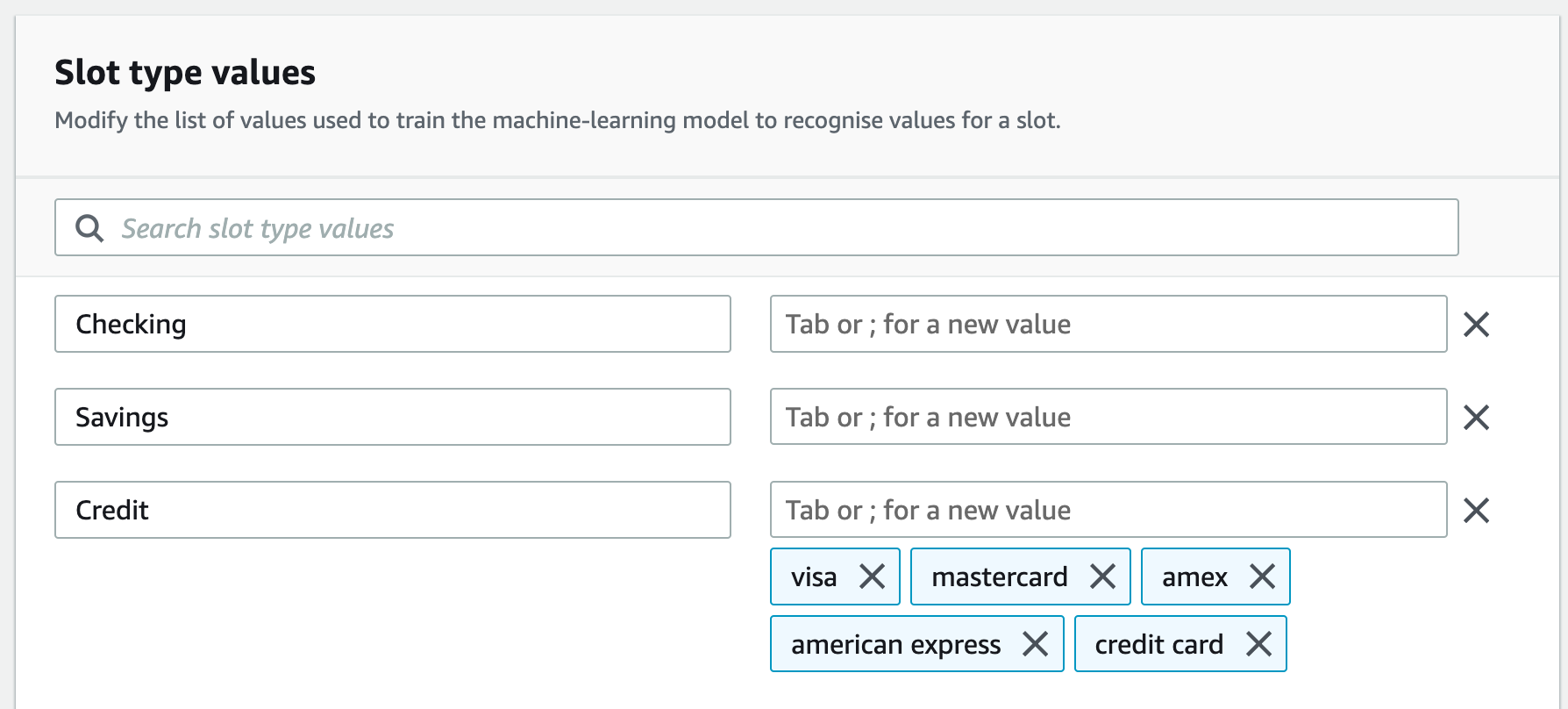
Now the slots are ready, time to build the intent for checking balance in the specified account type.
Step 5: Create the CheckBalance intent
-
Create a CheckBalance intent.
-
Add sample utterances:
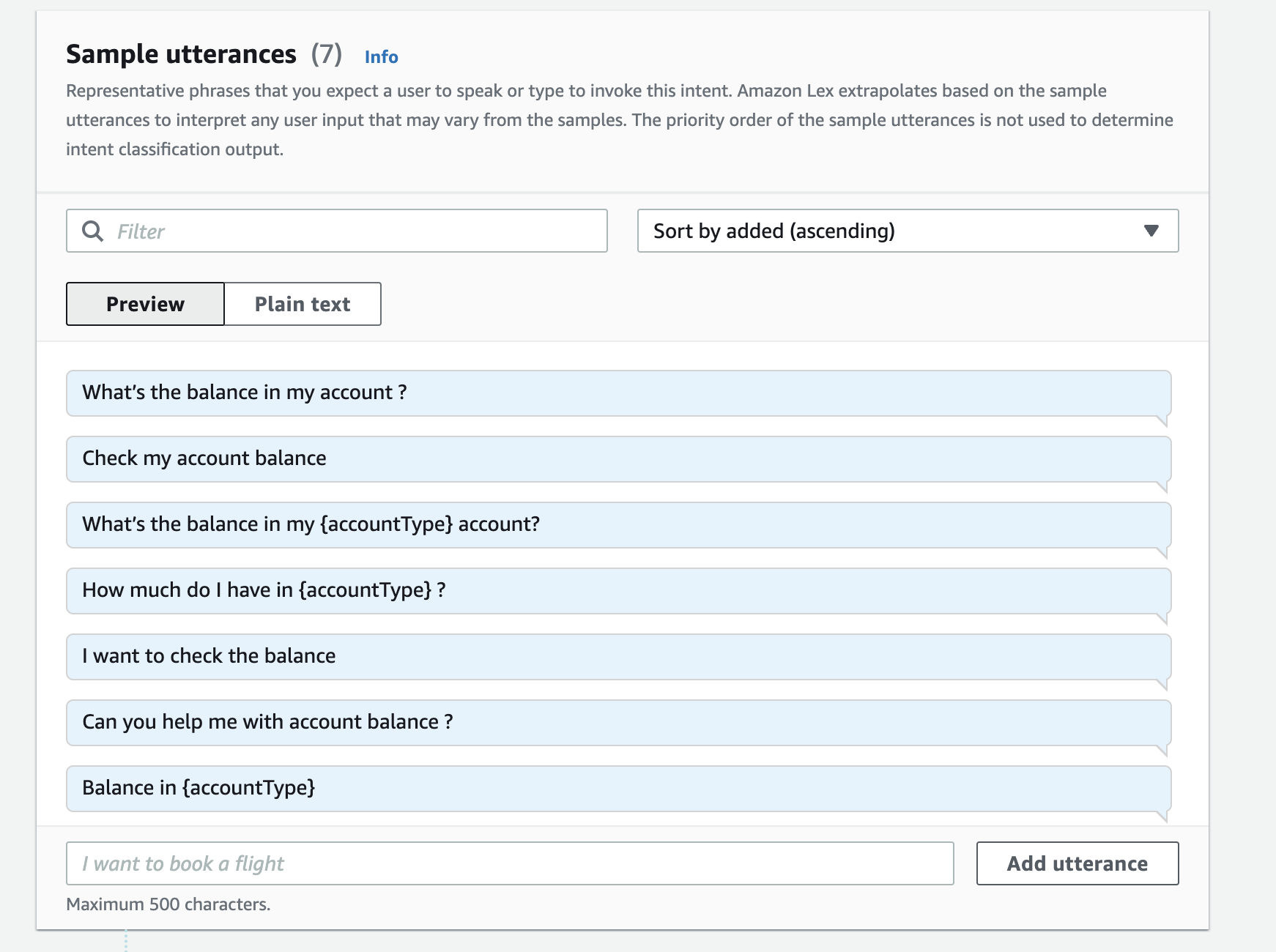
You'll notice that some of the utterances contains {accountTypes}. This is to trigger the Amazon Lex to look for slot values from the user's input.
- Add the "AccountType" slot to the intent's slots with prompts.
- Create another slot to get the user's birthday for verification purpose.

- Time to build and test:
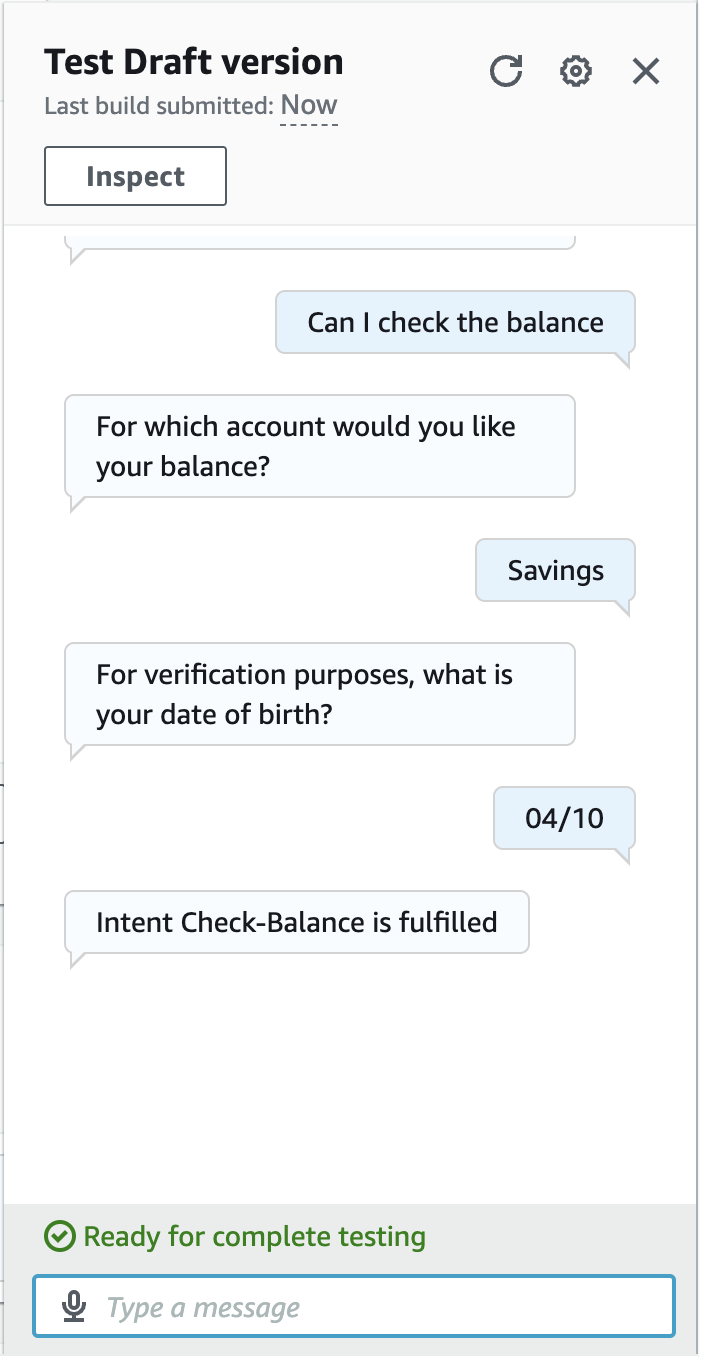
Step 6: Create a Lambda Function to Get Account Balance
Key notes ✏️:
What is Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a serverless service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. It's hightly scalable!
Here, I'll use Lambda function to help me get the user's account balance.
- Create a Lambda function from scratch and deploy the code:
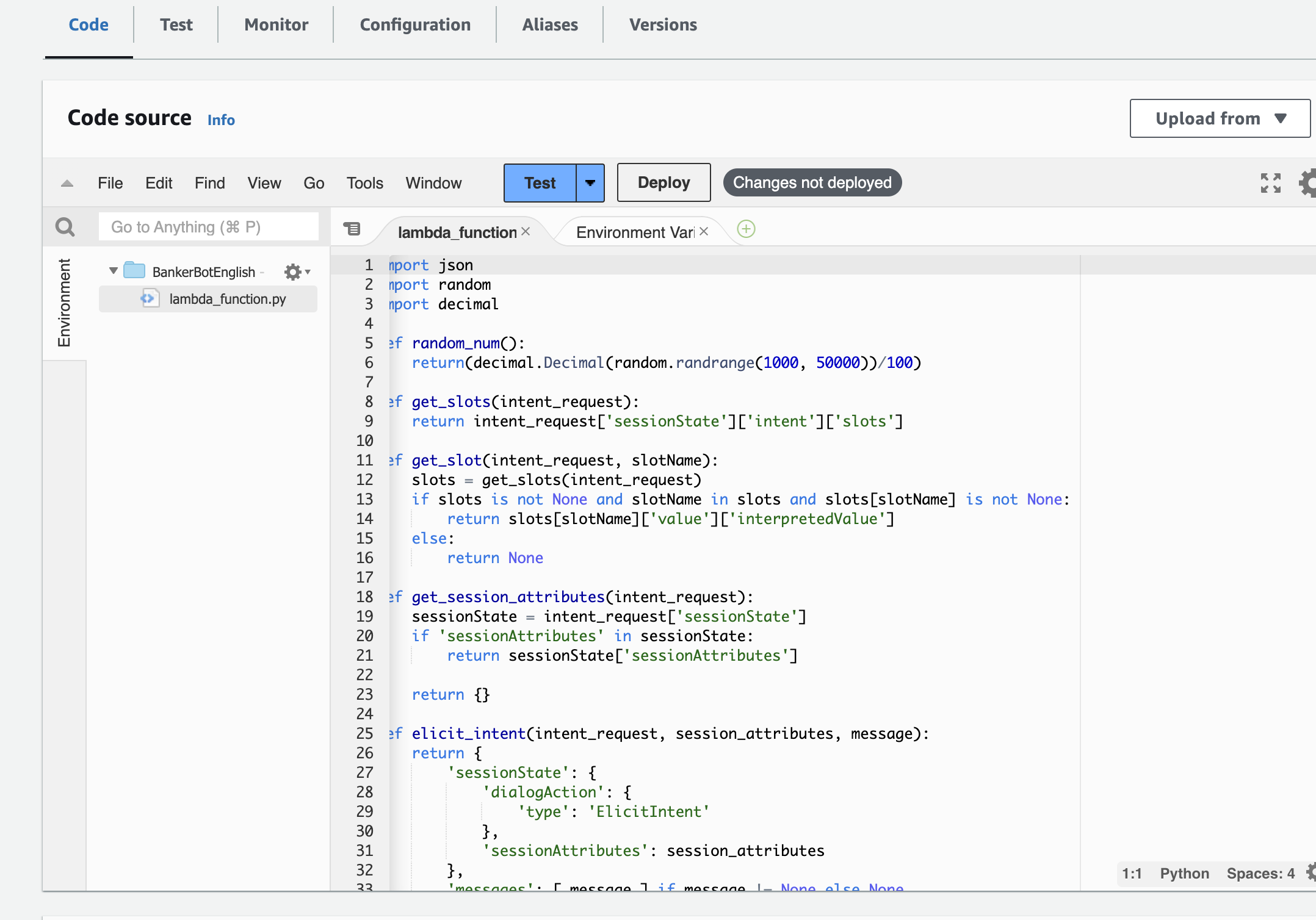
- Connect AWS Lambda with Amazon Lex
- Find the Alias on the left-side panel of the Lex console page and connect to the Lambda Function that just setup.
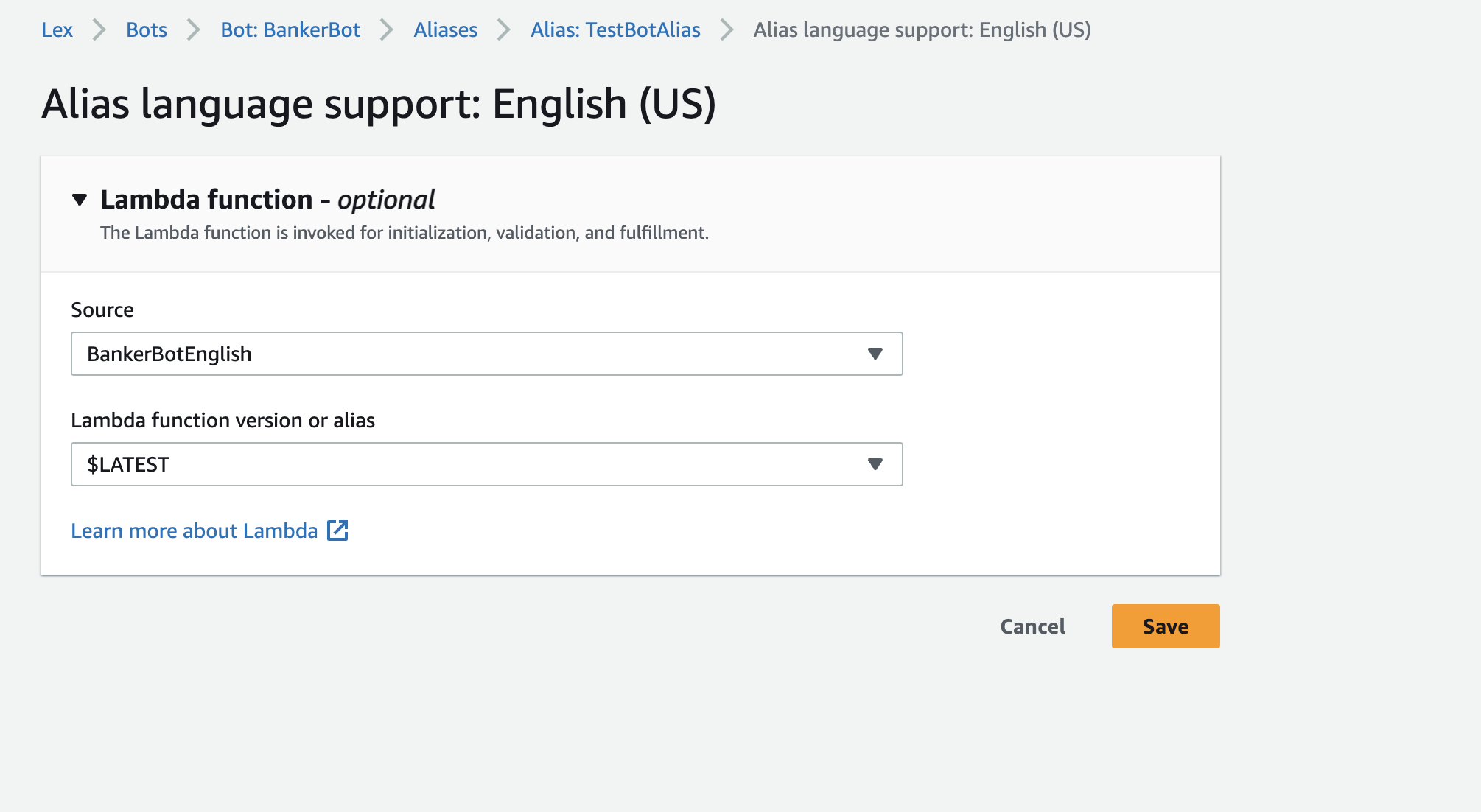
Key notes ✏️:
What is Alias?
Alias in Amazon Lex is like a pointer that points to a specific version of your bot. Saving your time in manually updating the connection to the newest version of the bot and telling other AWS services which version of the bot to connect.
- Connect the CheckBalance intent with the Lambda function
-
In the CheckBalance intent, update the Fulfilment setting.
-
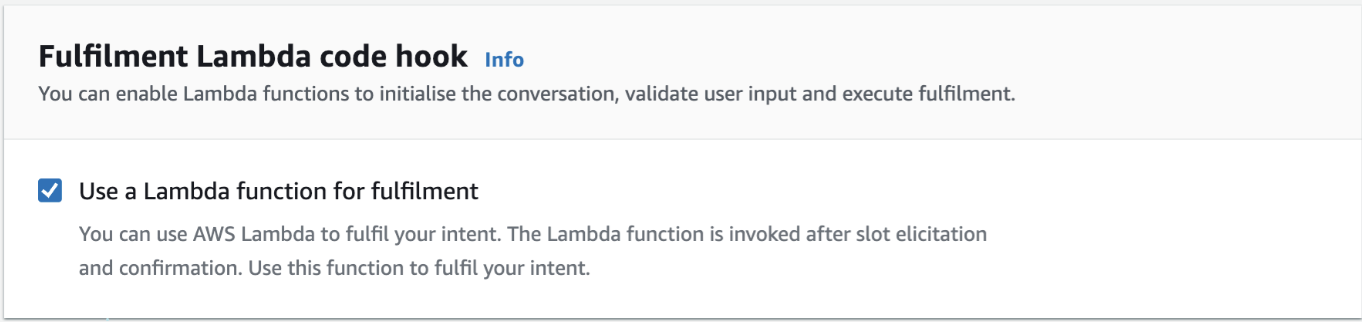
Within the fulfilment panel, activate the setting to Use a Lambda function for fulfilment.
-
Key notes ✏️:
What is fulfilment?
In Amazon Lex, fulfilment means completing the intent. After the bot received a user's account and the birthday for verification, the bot has all the information it needs and moves to fulfilment. This is where it will use the Lambda function to get the account balance and pass it back to the user.
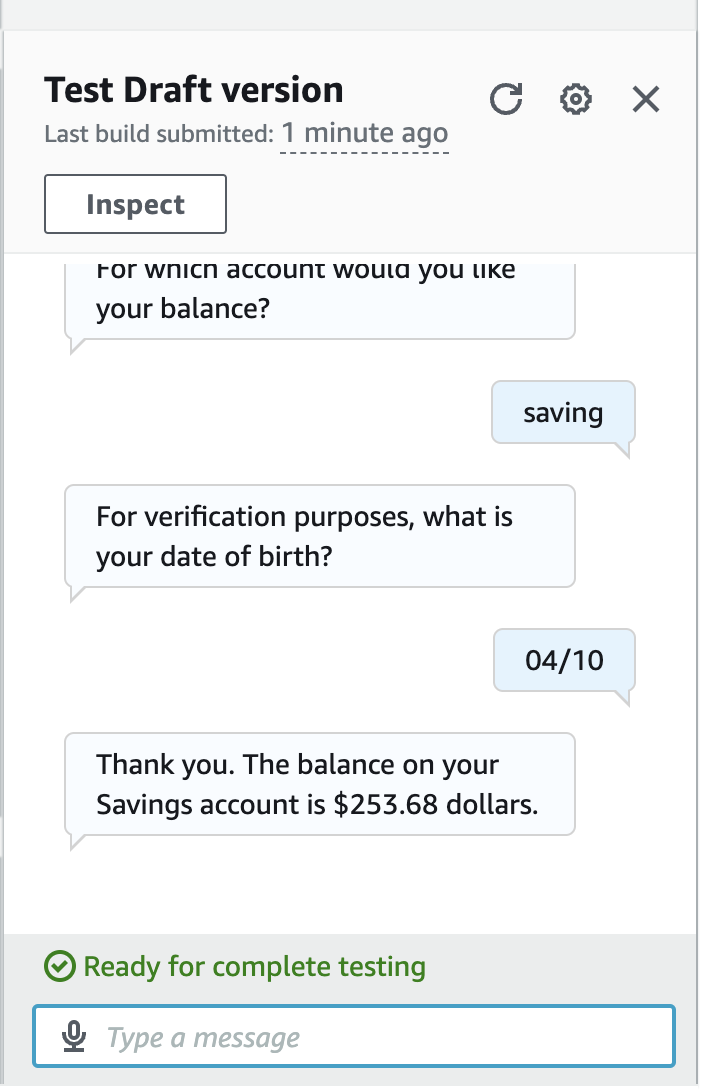
- Time to build and test!
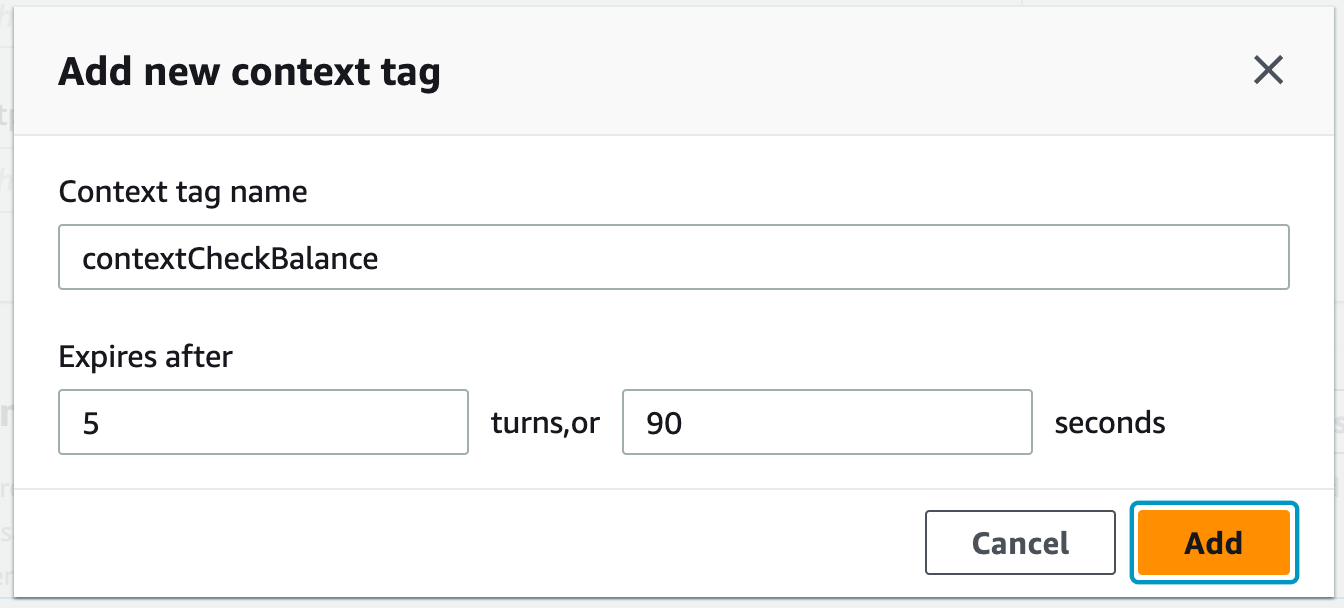
Step 6: Create the Output Context from CheckBalance
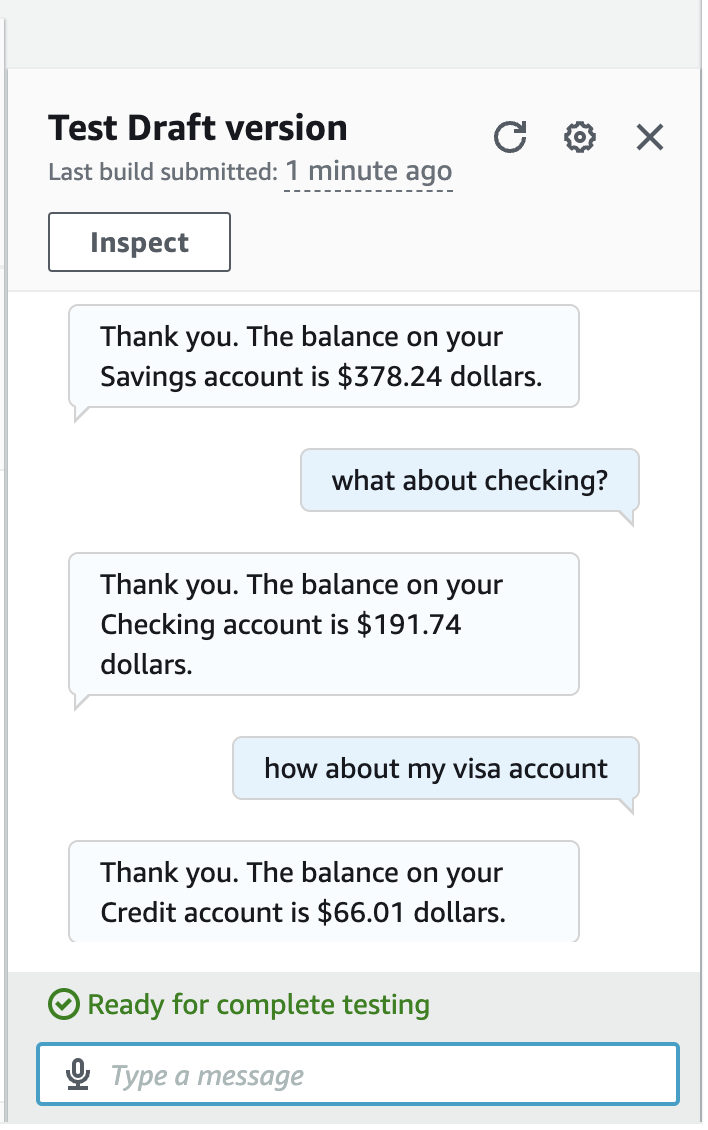
What if a user wants to continue to check other accounts' balances? How can we let the Chatbot skip the step of checking the birthday?
- In the CheckBalance intent page, create a new output Context tag.
Step 7: Create the FollowupCheckBalance intent and Apply the context
-
Create a new FollowupCheckBalance intent.
-
Apply the context to the "input contexts" in the context setting section.
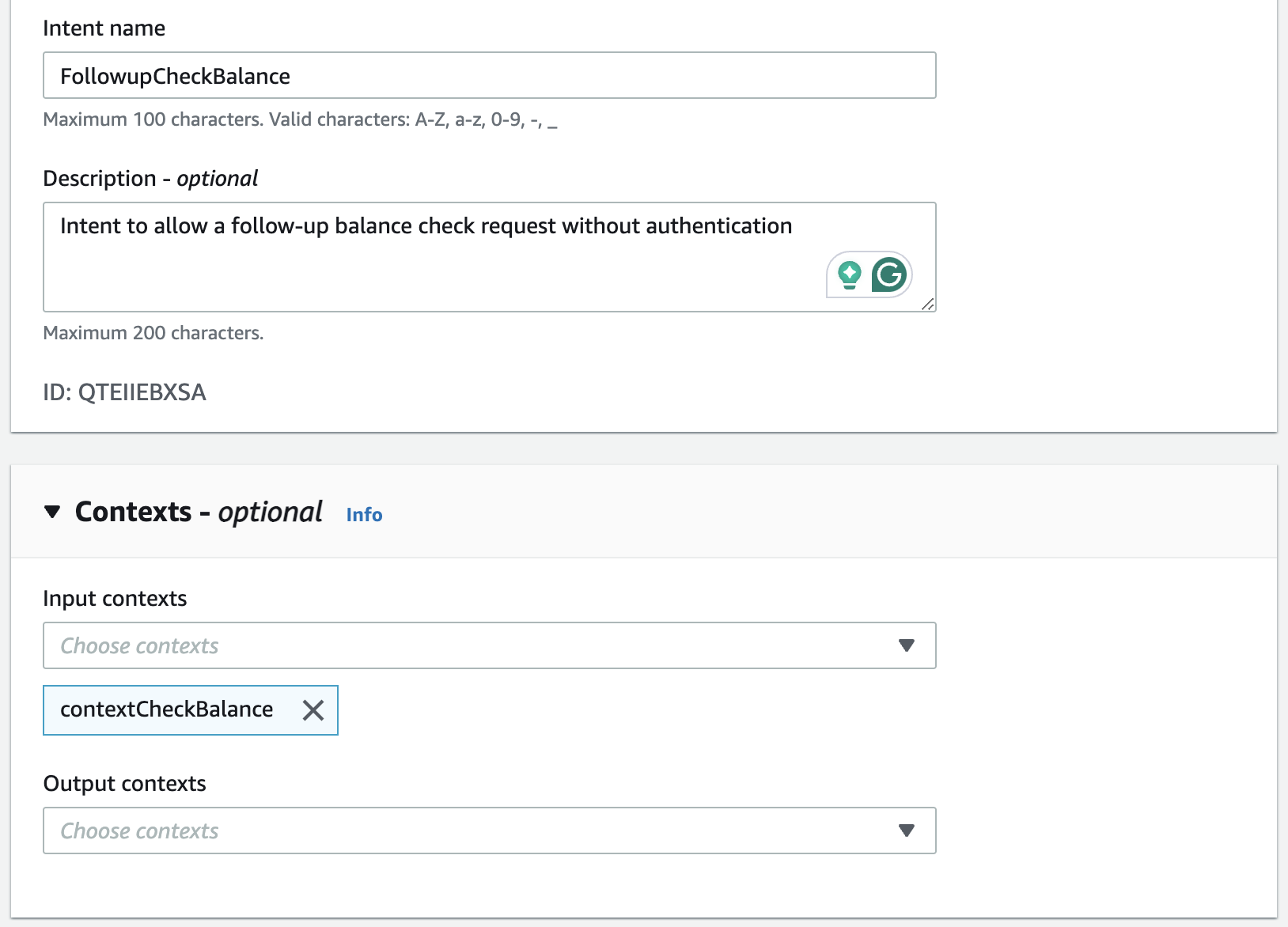
Now the bot is able to refer to info from the previous conversation when needed.
Step 8: Set the default value for DateOfBirth
- Set a default value to let the bot skip checking the birthday during follow up intent.
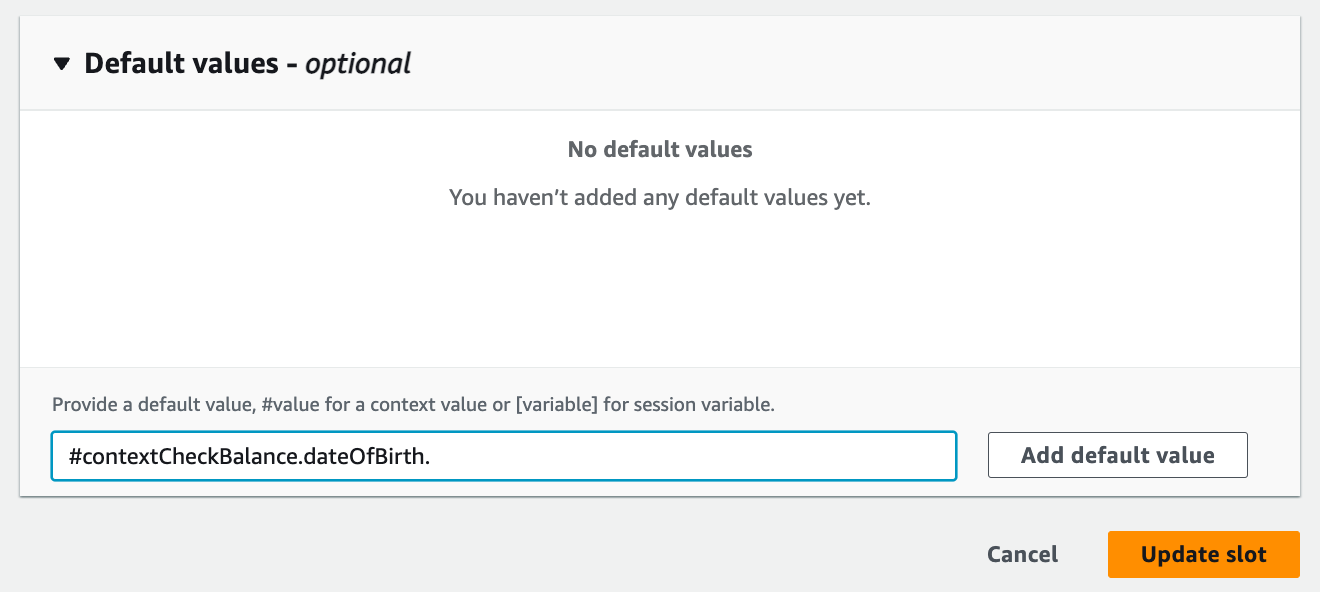
- Build and test:
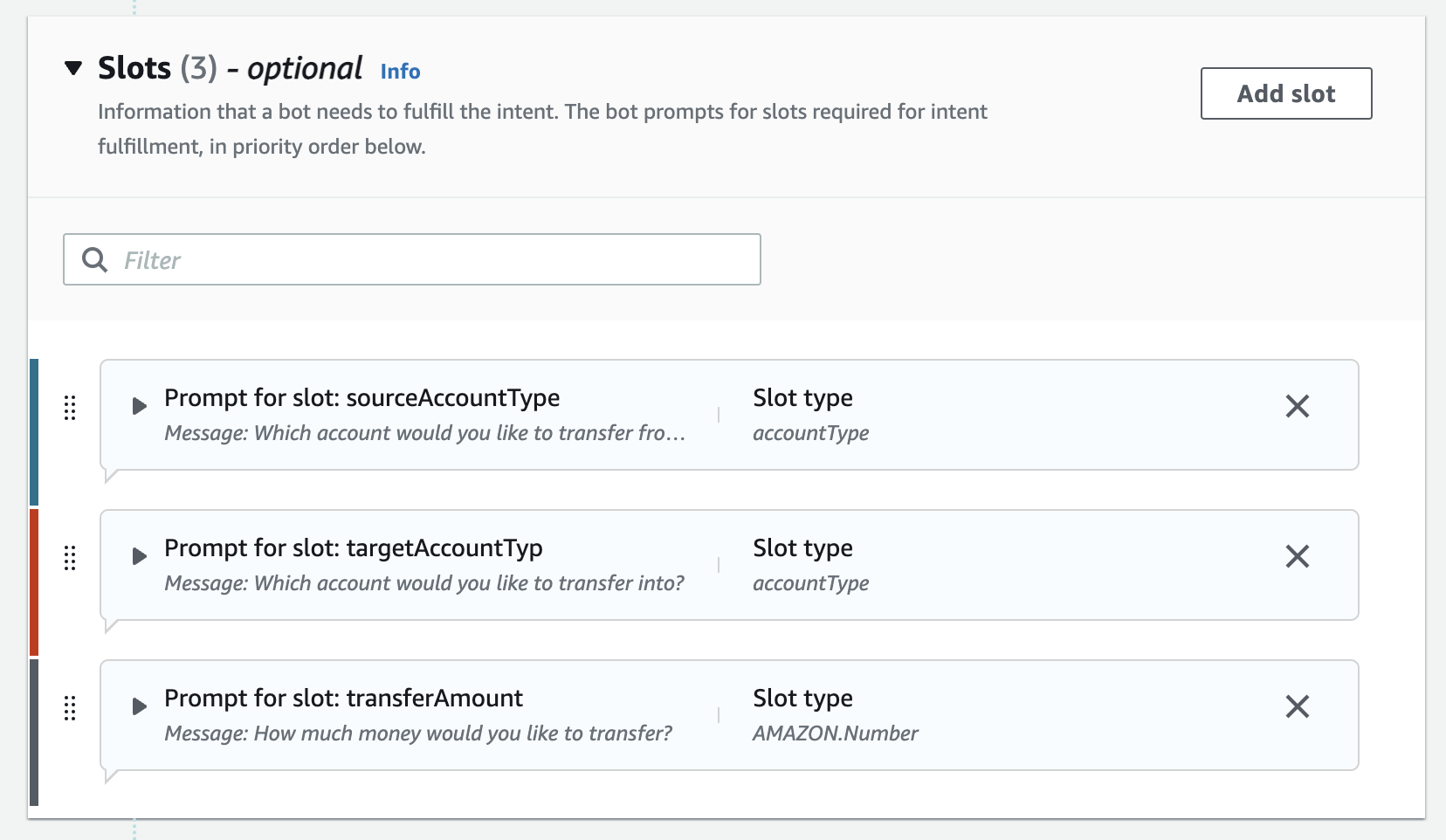
Step 9: Create the TransferFunds intent
Now it's time to set up the transfer funds feature.
- Create a new bank transfer intent.
- Add some sample utterances:
- Can I make a transfer?
- I want to transfer funds
- I'd like to transfer {transferAmount} from {sourceAccountType} to {targetAccountType}
- Can I transfer {transferAmount} to my {targetAccountType}
- Add slots and prompts:
- Add confirmation prompts Confirmation prompts helps to confirm with users wether they decide to process the request. This step helps to prevent the “”
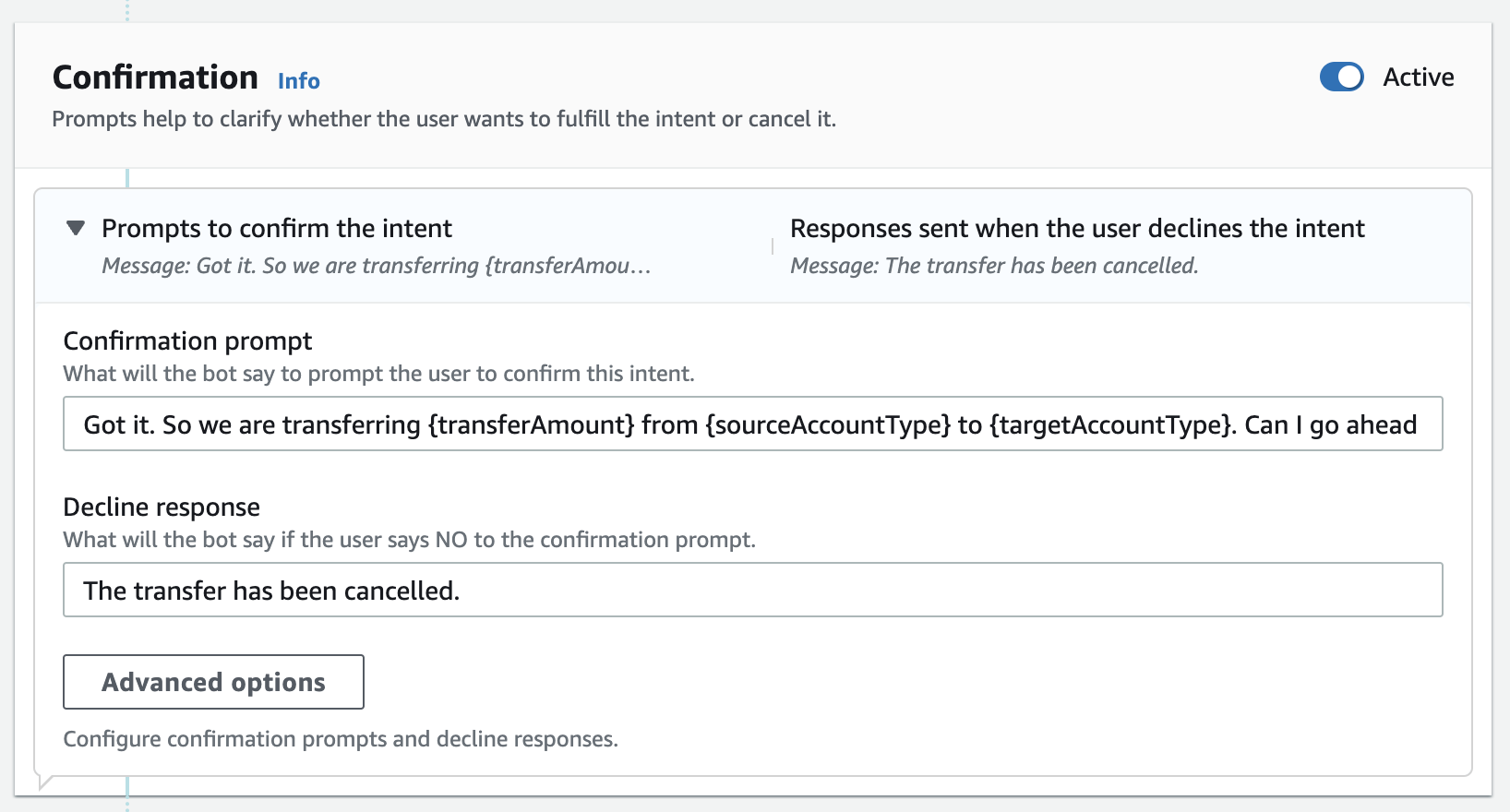
- Build and test:
- confirm to process
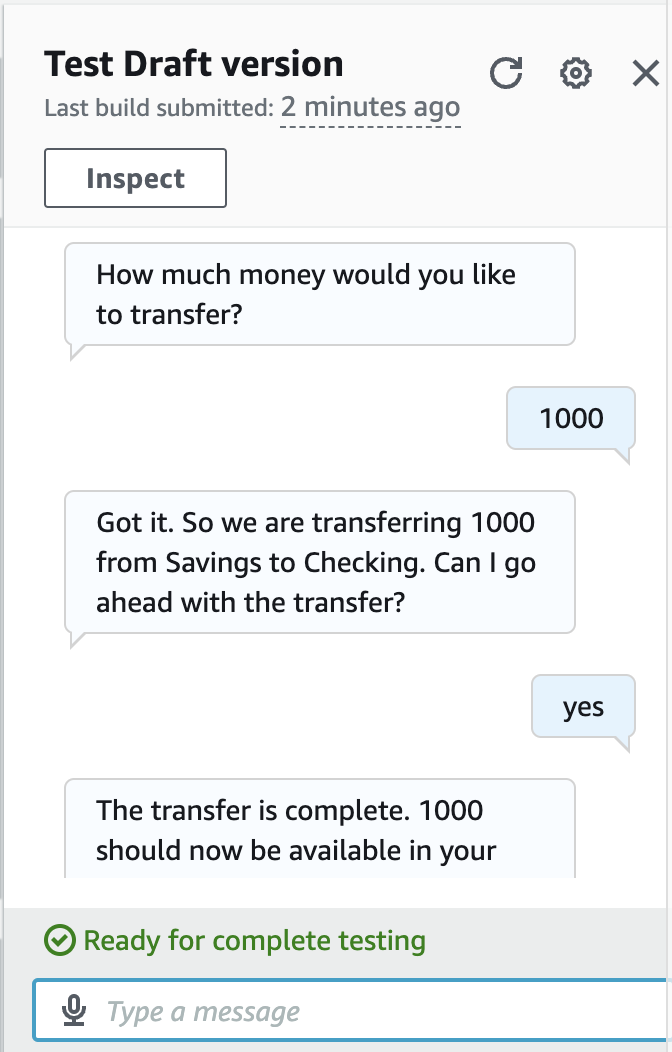
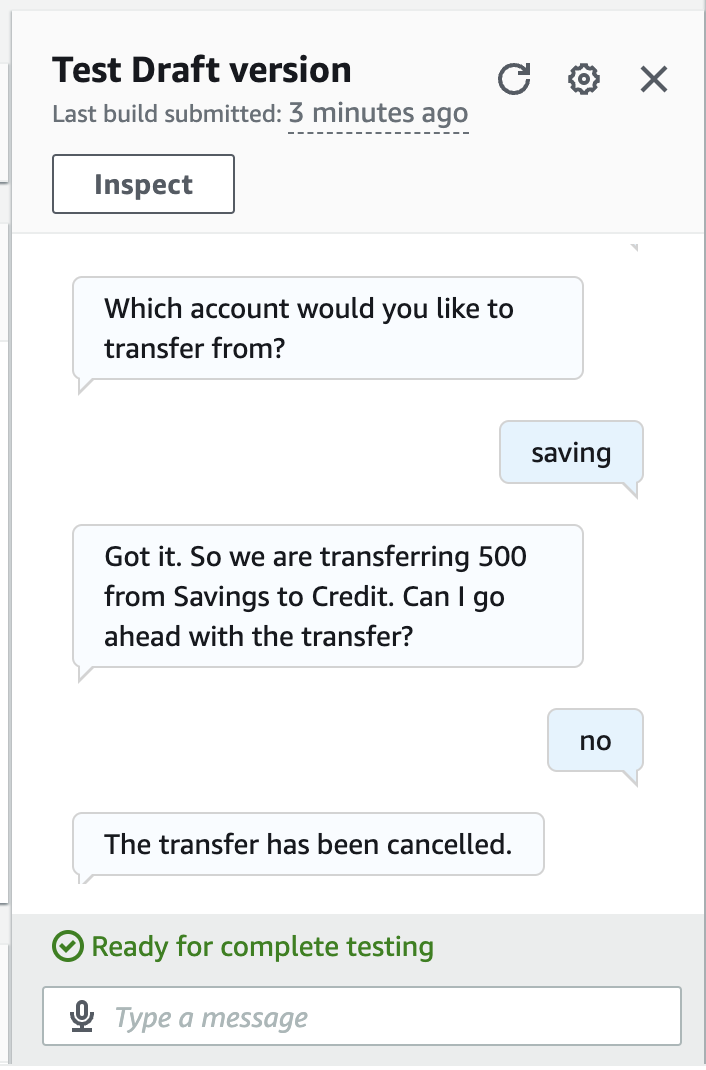
- cancel the process
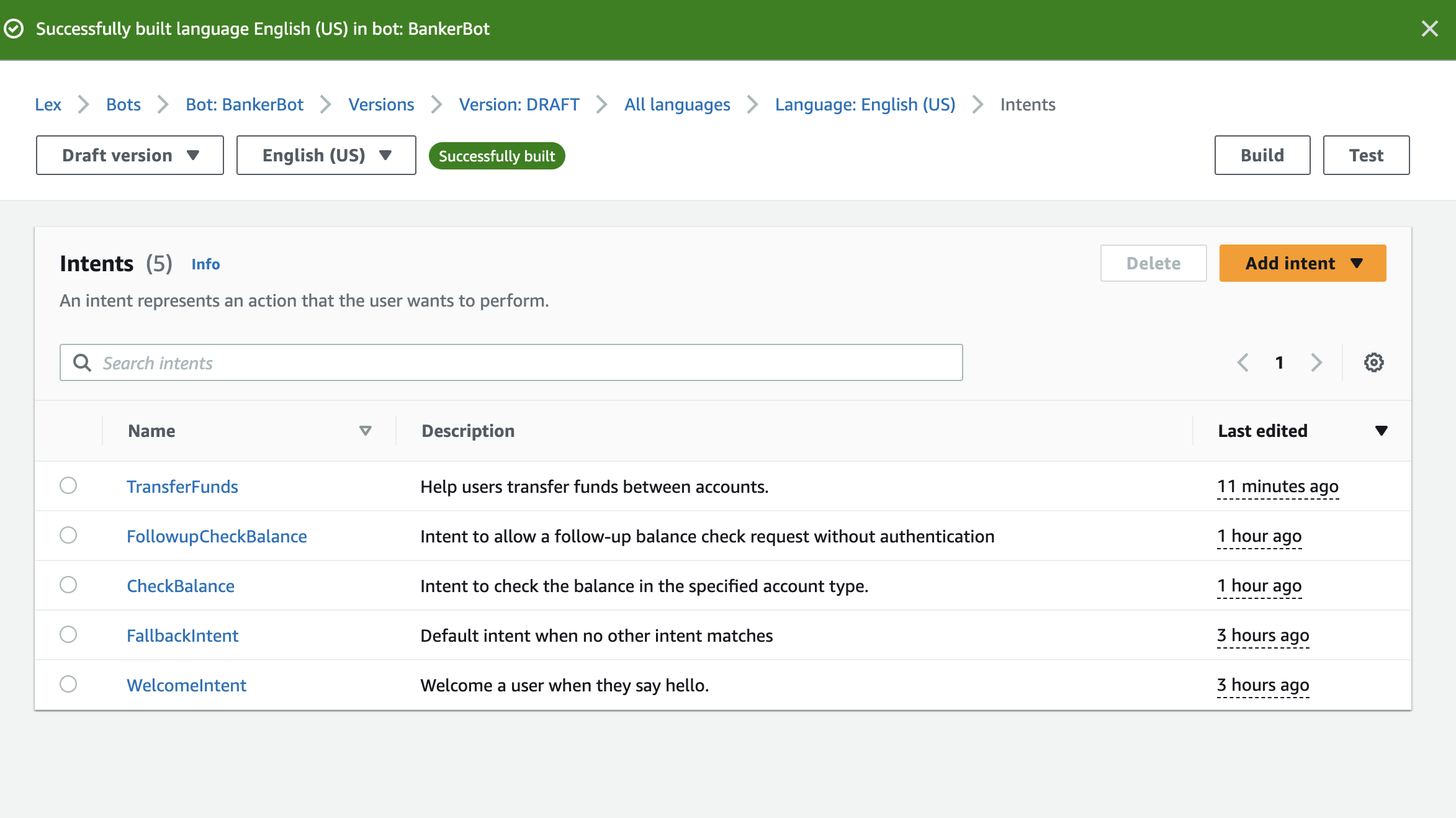
Have a look at all the intents that I created along the way
An error I ran into was...👀
I came across the error of failing to build the bot twice when I was trying to apply the "AccountType" slot types to the CheckBalance intent and when I was connecting the Lambda function to the Amazon Lex.
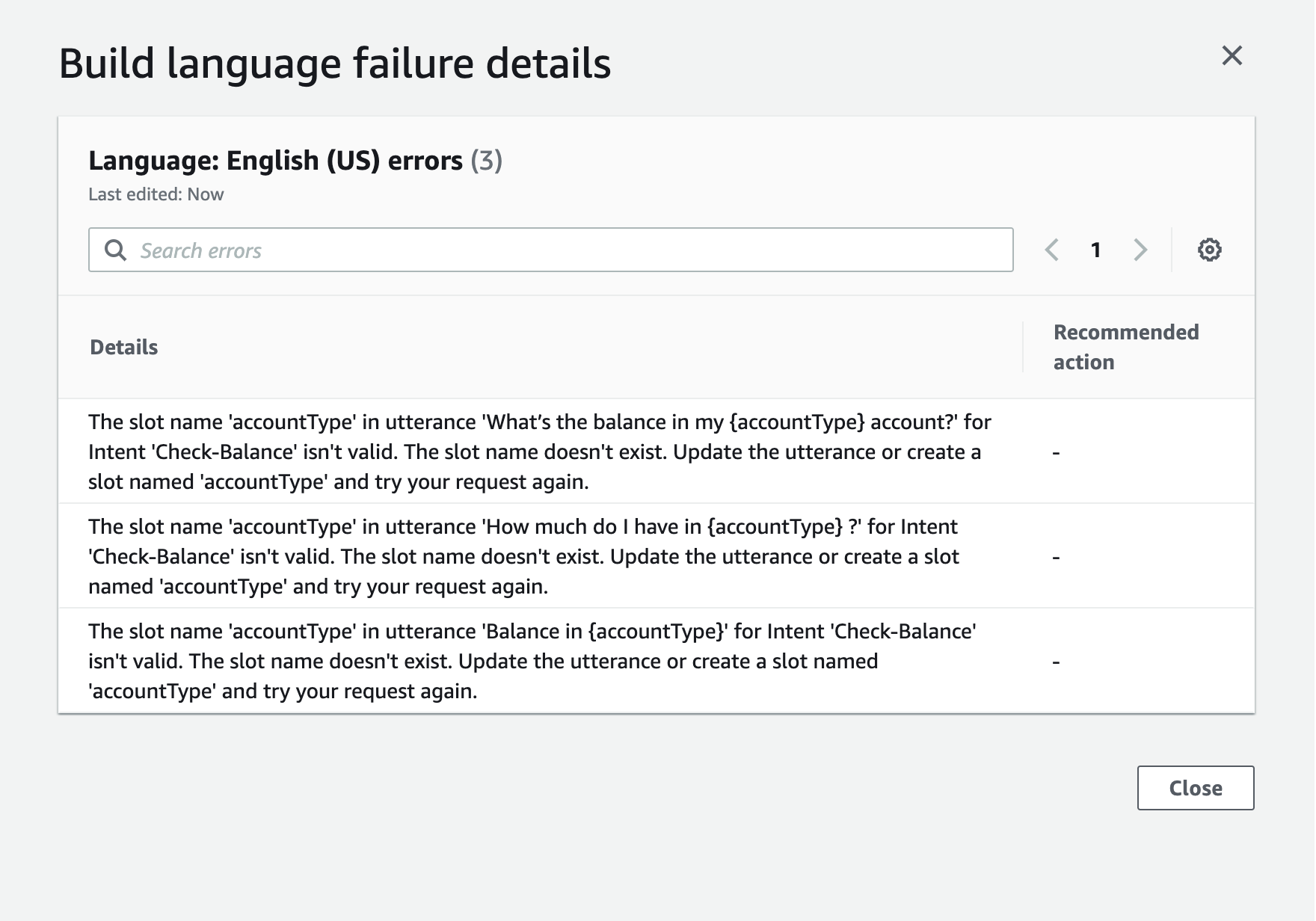
I found that the error occurred because the slot names in the utterances and the Lambda function's Python code mismatched the name in the Slot Types setting. Once I made all the names the same, the bot was successfully built.
What I leart from the error ✏️:
The Slot Types settings is crucial for the successful integration and functioning of the chatbot. It is important to make sure that slot names are consistent across different components of a chatbot system, such as in utterances, backend code (like Lambda functions).